
Cortisol levels are tightly controlled by a feedback mechanism involving the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. Cortisol influences sugar (glucose) metabolism, and has effects on bones, fat tissue, the cardiovascular system, the immune system and is involved in the “fight or flight” response to stress. Medications include prednisone and dexamethasone.Ĭortisol A glucocorticoid or corticosteroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Consists of medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain.īuffalo Hump Hump-like collection of fat between and above the shoulder blades.Ĭhronic Term used to describe long-lasting diseases or conditions.Ĭognitive Mental process of thought, perception, reasoning, intuition and memoryĬongenital Term used to describe something present at birth, especially an abnormality.Ĭorticosteroids Hormones produced by the cortex of the adrenal glands also, a class of such hormones used as medications for inflammatory conditions such as asthma and arthritis.

Produced in the testicles in the male also found in small amounts in the female.īenign Term meaning essentially harmless not progressive.īlood Pressure Constant force placed on the walls of the arteries.īrain Stem Portion of the brain that connects the hemispheres with the spinal cord. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce and release cortisol into the blood stream.Īdrenal Glands Endocrine glands located on top of the kidneys, that produce a range of hormones, including epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, the corticosteroid hormones and some androgens.Īldosterone Adrenal hormone that affects the body’s handling of sodium, chloride, and potassium and helps regulate blood pressure.Īndrogen A hormone such as testosterone and androsterone responsible for the development of male characteristics.
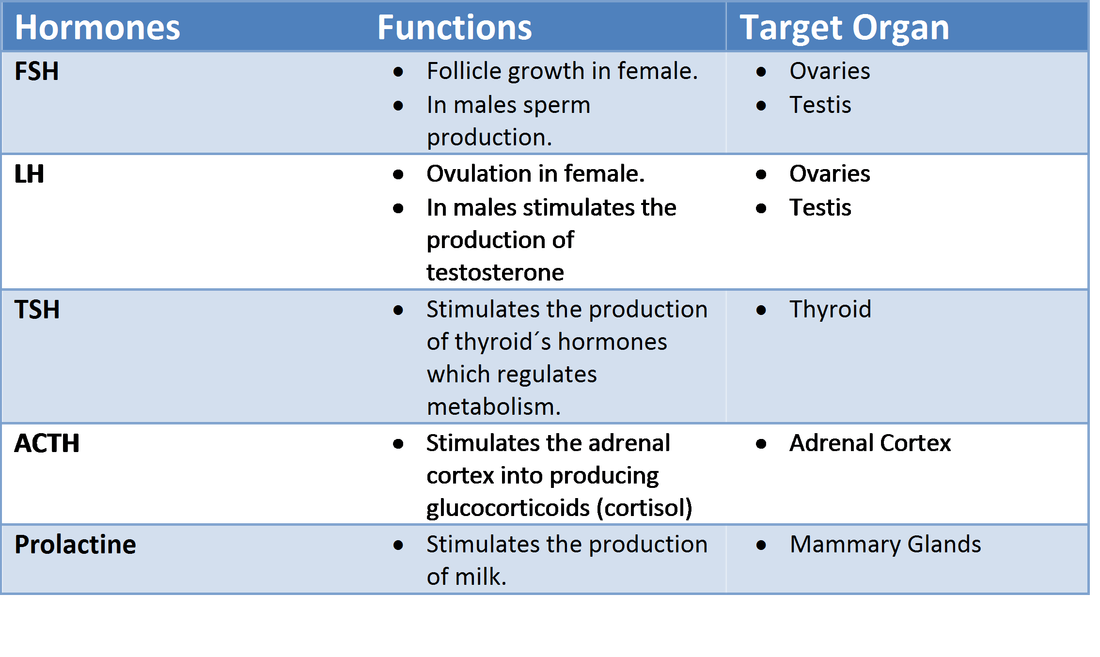

ACTH An abbreviation for the adrenocortiotropic hormone secreted by the pituitary gland.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
